What is Periodontology?
Periodontology is the branch of dentistry that focuses on the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases that affect the supporting structures of the teeth, including the gums, bones, and connective tissues.
Gum disease is inflammation of the gum tissues that support the teeth. It is typically characterized by symptoms such as redness, swelling, bleeding, gum recession, and tooth mobility.
The most common cause of gum disease is the accumulation of plaque, which can harden into calculus or tartar if not removed by proper dental hygiene practices like brushing and flossing. Gum disease can be treated if diagnosed early.
İçindekiler

What are the types of periodontal disease?
Periodontal diseases are typically referred to as gum diseases, but it is a more general term that encompasses any disease that affects the supporting tissues of the teeth.
Periodontal diseases can occur in different forms, including:
- Gingivitis: the most common type of periodontal disease that is characterized by inflammation of the gum tissues, but without any bone or gum loss. It can be treated with proper dental hygiene practices.
- Chronic periodontitis: the most common type of periodontal disease that is characterized by inflammation of the gum tissues, gum recession, and the formation of deep pockets around the teeth that can lead to bone and tooth loss. It can be managed with dental hygiene practices, scaling and root planing, and periodontal surgery.
- Aggressive periodontitis: a rare but severe form of periodontal disease that progresses rapidly, affecting young individuals, and causing rapid gum recession and tooth mobility. It can be treated with dental hygiene practices and periodontal surgery.
- Periodontal abscess: a type of abscess that forms due to the presence of pus in the periodontal pocket. It can be treated with periodontal pocket cleaning and antibiotics.
- Necrotizing periodontal disease: a severe form of periodontal disease that causes oral lesions, tissue death, and bone loss in the periodontal pocket. It can be treated with antibiotics, dental hygiene practices, and periodontal surgery.
The treatment of these diseases can vary depending on factors such as starting treatment early and regular dental care. Therefore, it is important to have regular check-ups with your dentist and take care of your dental hygiene.
What are the main symptoms of gum disease?
- Swelling, redness, or bleeding of the gums
- Itching, burning, or sensitivity of the gums
- Receding gumline or visible teeth
- Increased gaps between teeth or loose teeth
- Formation of gum pockets
- Bad breath or bad taste in the mouth
- Tooth sensitivity or pain when chewing
- Formation of abscess or fistula in the gums
- If you experience one or several of these symptoms, it is recommended to consult your dentist. Gum diseases that are diagnosed and treated early can be controlled without causing serious problems such as tooth loss.

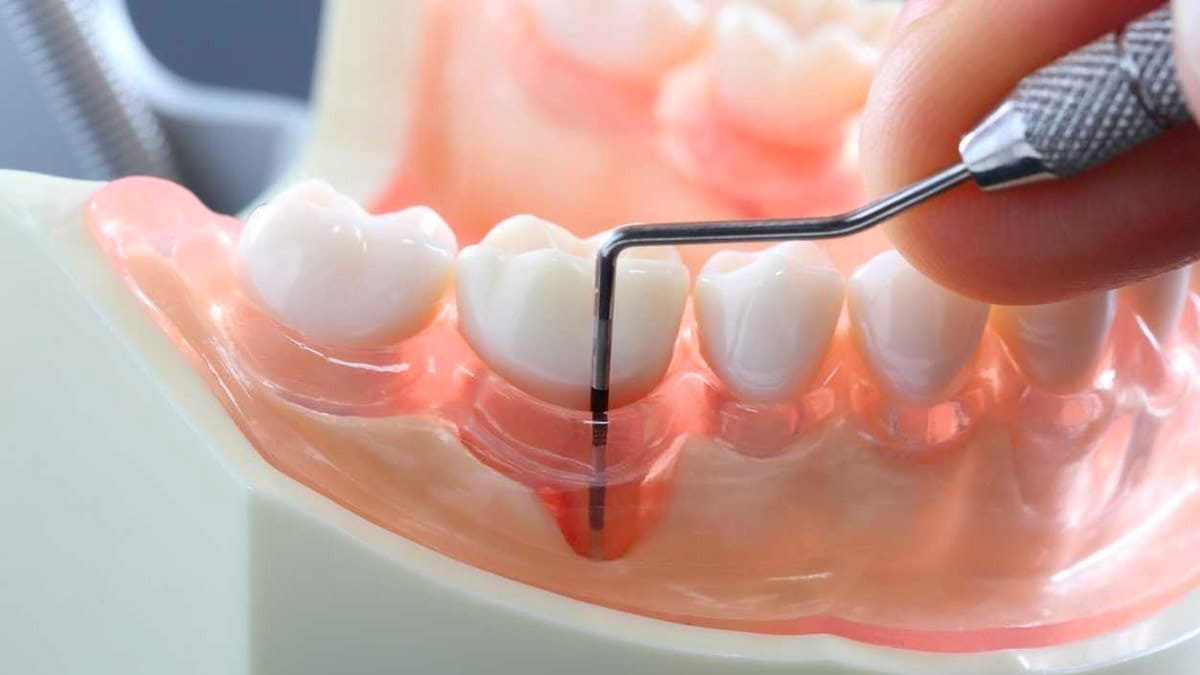
What causes gum disease?
Gum disease is an infection typically caused by a bacterial film that accumulates on the tooth surfaces, known as plaque.
Gum disease is usually caused by bacterial infections from a film called plaque that accumulates on the surfaces of teeth. Plaque is made up of food and drink residues that need to be removed by brushing teeth. If plaque builds up on teeth for a long time, bacteria can damage the gums and cause gum disease.
Other causes may include genetic factors, hormonal changes (e.g. pregnancy), smoking, stress, improper brushing technique, improper dental procedures, systemic diseases (e.g. diabetes), and some medications (e.g. antidepressants, antihistamines, and blood pressure medications).
Controlling the risk factors that cause gum disease and getting regular dental cleanings can help prevent gum disease.
How is gum disease treated?
The treatment of gum disease can vary depending on the severity and type of the disease. Treatment is more successful when the disease is diagnosed and treated early. Here are the methods for treating gum disease:
Professional dental cleaning: The first stage of gum disease treatment is usually a professional dental cleaning. A dentist or dental hygienist can clean the buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth, stopping the progression of gum disease.
Root planing and scaling: In cases where gum disease has progressed, a dentist may perform a root planing and scaling procedure to clean bacteria from the gum pockets. This procedure involves smoothing the root surfaces of the tooth and reducing the size of the gum pockets.


Antibiotic therapy: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to kill the bacteria causing gum disease. This treatment is often used in conjunction with root planing and scaling.
Surgical procedures: If gum disease has advanced, a dentist may perform a surgical procedure such as bone grafts, gum grafts, or tooth extraction.
The best way to treat gum disease is early diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, it is important to attend dental check-ups as recommended by your dentist, regularly brush and floss your teeth. Additionally, healthy lifestyle choices such as a healthy diet and not smoking can also reduce the risk of gum disease.
What are some frequently asked questions about gum disease?
The most common cause of gum disease is bacteria. When oral hygiene is insufficient, bacteria that accumulate on teeth can form a layer of plaque below the gum line. This plaque can lead to gum inflammation (gingivitis) and, in more advanced cases, gum disease (periodontitis).
The symptoms of gum disease include red, swollen and bleeding gums, bad breath, gum recession, and loose teeth.
To prevent gum disease, you should regularly brush your teeth, use dental floss, have regular checkups with your dentist, and follow a healthy diet program.
The treatment for gum disease can vary depending on the severity of the disease. Typically, tartar and plaque around the teeth are removed and the gum pockets are treated. In more advanced cases, gum surgery may be necessary.
Gum disease is not contagious, but the risk of developing gum disease may be higher among family members.
Regularly brushing your teeth, using dental floss, having regular dental check-ups, not smoking, and following a healthy eating program can help reduce your risk of gum disease.
Yes, the risk of developing gum disease may increase during pregnancy. Therefore, it is recommended for pregnant women to have regular dental check-ups.
Treatment of gum disease can be painful, but the use of anesthesia can significantly reduce pain. Additionally, your dentist can use various methods to minimize pain.
The recovery time after gum disease treatment can vary depending on the severity of the disease, the type of treatment, and individual factors. In mild cases where treatment is not extensive, the recovery time can range from a few days to a few weeks. However, in more serious cases of gum disease, the recovery time may be longer and sometimes it can even become a chronic condition.